What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a fascinating and emerging field that has made enormous progress in recent years and is increasingly influencing various areas of our lives. AI refers to the ability of machines or computers to imitate or even surpass human-like intelligence.
In this article, we take a closer look at the concept of Artificial Intelligence, its history, its applications, its impact on the industry with its advantages and disadvantages, and its role in the future.
The History of Artificial Intelligence
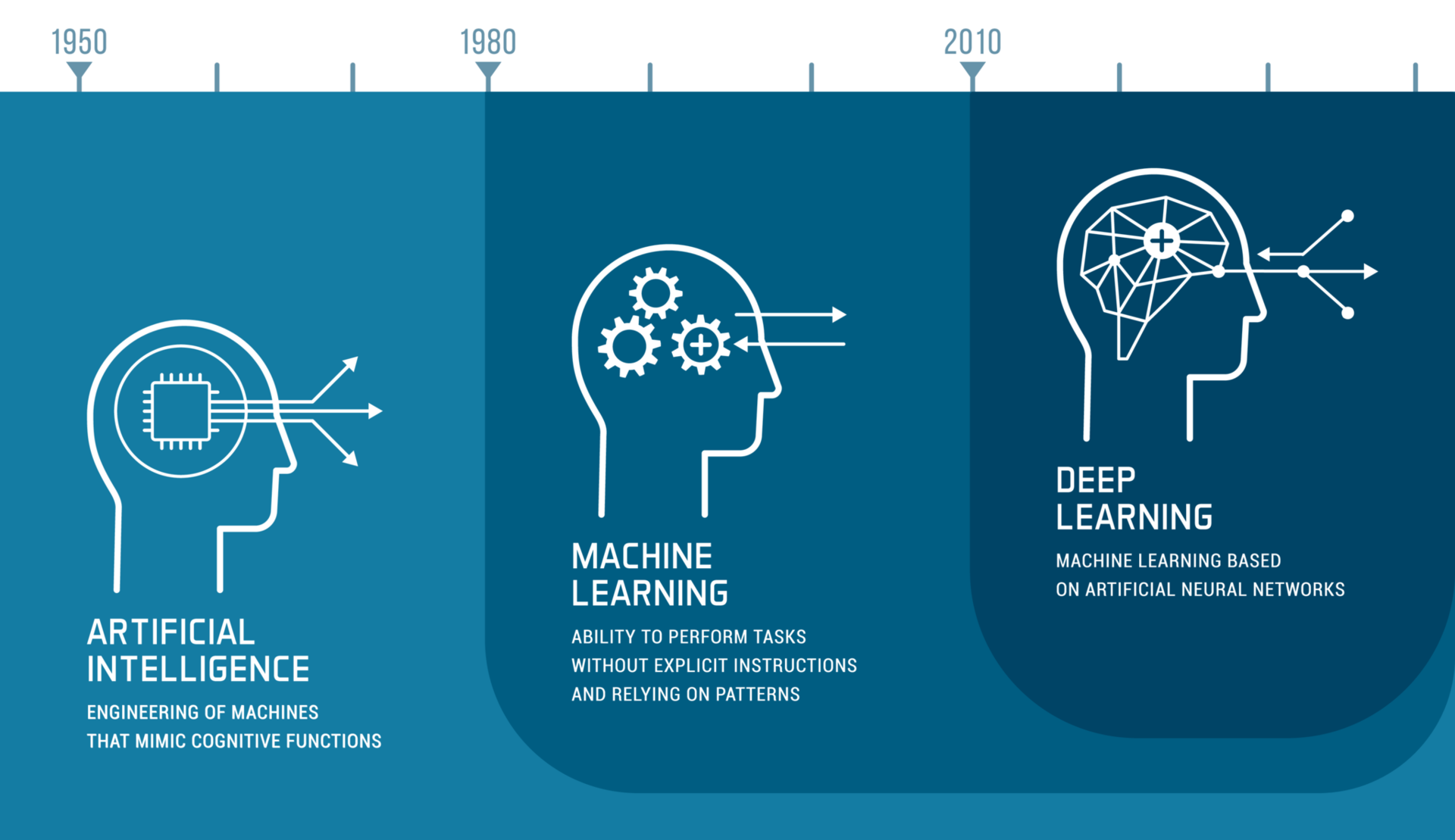
The idea of artificial intelligence is not new and dates back to antiquity, when mythical automatons and mechanical figures appeared in stories and legends. However, the real breakthrough in the development of AI occurred in the 20th century. In 1956, the term "artificial intelligence" was first coined by John McCarthy, one of the pioneers in this field. McCarthy organized a conference at Dartmouth College, which laid the foundation for the research and development of AI.
In the following decades, there were repeated advances in AI research, but also setbacks. In the 1980s, AI experienced the so-called "AI Winter," during which interest and funding declined sharply. However, in recent years, AI research has experienced a renewed boom, thanks to advances in computing power, the availability of large amounts of data, and new algorithms.
The Functionality of Artificial Intelligence
The functioning of AI is based on the concept of machine learning, which enables computers to learn from experience and adapt without being explicitly programmed. By training models with large amounts of data, AI systems can recognize patterns and make predictions.
The terms Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) are often used interchangeably. In fact, however, DL is a subset of ML, and ML is a subset of AI.
AI is a general term and describes the approach of using machines to mimic intelligent human behavior to solve problems. AI are software applications that can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence.
ML is the technology used to achieve AI. ML are applications that are capable of learning independently and solving tasks without a pre-programmed solution path.
DL is the advancement of ML. The technology is based on the use of so-called neural networks. DL are special ML algorithms that are modeled after the human brain (artificial neural networks).
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is based on the concept that machines, through the use of algorithms and data, are capable of performing tasks that are typically assumed to require human intelligence. Examples include speech recognition (Alexa, Siri), image recognition, decision-making, and much more.
There are two main types of artificial intelligence: weak AI (English: Narrow AI) and strong AI (English: General Artificial Intelligence). Weak AI refers to systems that are limited to specific tasks or applications, such as chatbots that support customer service. Strong AI, on the other hand, refers to systems that possess general intelligence and are capable of handling a wide range of tasks, comparable to human intelligence. Strong AI is still in its early stages and remains a goal of AI research.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Industry
The impacts of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on the industry are profound and are changing the way companies operate, produce, and interact. Here are some of the key impacts:
- Economy: AI can help automate and optimize processes in the industry. This leads to a significant increase in efficiency and a reduction in production costs, as tasks are performed more precisely and quickly.
- Quality control: AI systems can perform quality controls in real-time by analyzing images and data. This allows companies to detect and sort out defective products early, leading to higher product quality and lower rejection rates.
- Predictive maintenance: AI can be used to monitor the condition of machines and equipment and provide early warnings of potential failures. This allows companies to better plan maintenance work, reduce downtime, and lower costs.
- Customer personalization: In the manufacturing industry, AI-driven systems can be used to customize products according to the individual requirements and preferences of customers. This enables tailored products and services that increase customer satisfaction.
- Logistics and supply chain optimization: AI can help improve supply chain planning and optimization. This enables better inventory management, routing optimization, and tracking of products during transport.
- Development of new products: AI can support companies in identifying market trends and customer needs. By analyzing data and feedback, AI can help develop innovative products and services that are successful in the market.
- Workforce and training: With the introduction of AI in the industry, the requirements for the workforce are changing. New professions in the field of AI development and integration are emerging, while some traditional tasks are being replaced by automation. Companies need to invest in training their employees to ensure they can effectively use the new technologies.
- Competitiveness: Companies that integrate AI into their processes early can strengthen their competitiveness. Efficiency gains and product innovations can help gain market share and increase profitability.
- Risks and challenges: Despite the advantages, the introduction of AI also poses challenges, such as data protection and security concerns, ethical questions related to autonomous systems, and the need to manage the impacts on the workforce.
Overall, it is evident that Artificial Intelligence plays a key role in the transformation of the industry. Companies that recognize and wisely utilize the potentials of AI can increase their efficiency, reduce costs, and strengthen their competitiveness. However, it is important to carefully address the challenges associated with this technology to ensure it is used within an ethically acceptable and legally secure framework.

